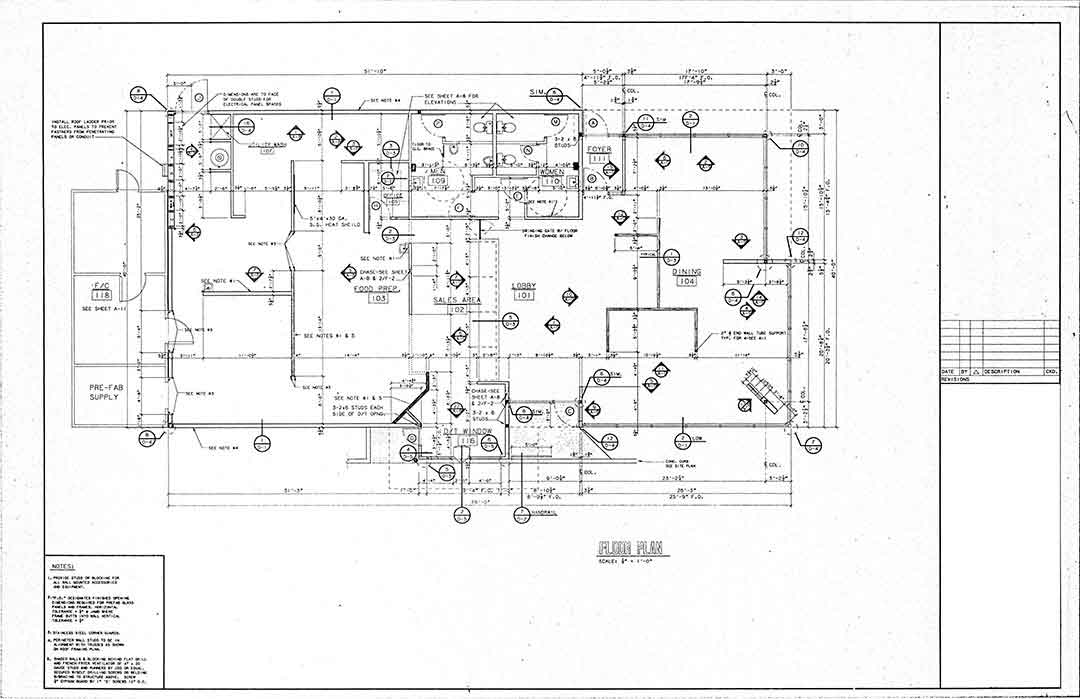
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) refers to the essential building systems responsible for heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), electrical wiring, lighting, and plumbing networks in a construction project.
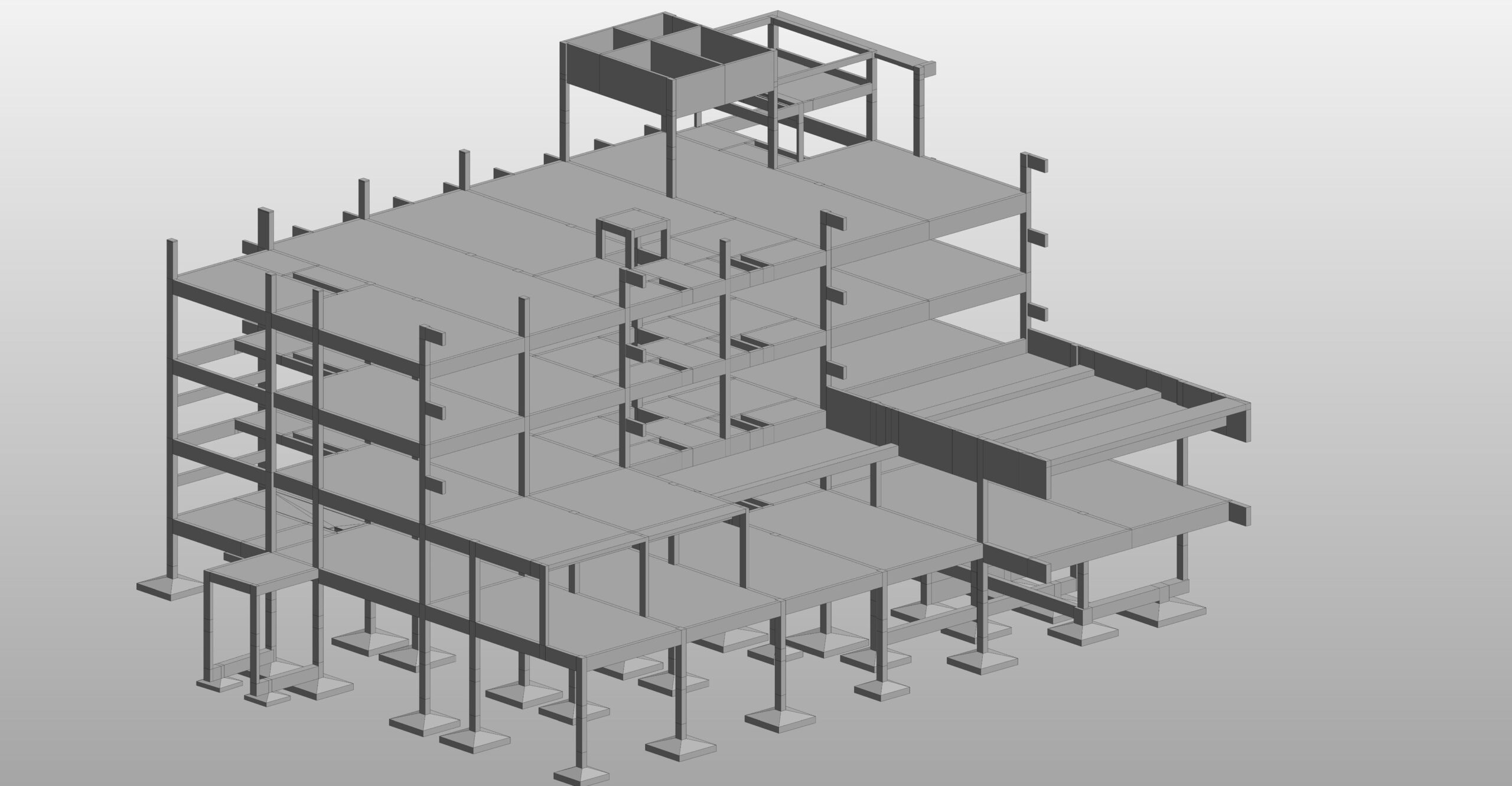
Using BIM (Building Information Modeling) for MEP design improves coordination, efficiency, and accuracy, ensuring all systems work together seamlessly within a building.
Key Components of MEP in BIM
1. Mechanical (HVAC Systems)
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
- Air ducts, chillers, cooling towers, and ventilation shafts.
- Ensures thermal comfort and air quality in the building.
2. Electrical Systems
- Power distribution, lighting, and emergency systems.
- Wiring, electrical panels, transformers, and fire alarms.
- Ensures energy efficiency and safety compliance.
3. Plumbing Systems
- Water supply, drainage, and sanitary systems.
- Fire suppression (sprinklers) and gas piping.
- Ensures efficient water management and waste disposal.
Benefits of BIM for MEP Design
✅ Clash Detection & Conflict Resolution
- Identifies clashes between MEP, structural, and architectural elements.
- Prevents costly rework and design modifications.
✅ Improved Collaboration
- MEP teams can work alongside architects and structural engineers.
- Cloud-based platforms like BIM 360, Trimble Connect, and Aconex enable real-time collaboration.
✅ Accurate Quantity Takeoff & Cost Estimation
- Extracts precise material quantities, reducing waste and cost overruns.
✅ Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
- BIM allows energy simulations to optimize HVAC and electrical systems.
- Helps meet LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification requirements.
✅ Faster Installation & Maintenance
- Contractors use BIM models for prefabrication and on-site installation.
- Facility managers use the BIM model for maintenance and future renovations.