BIM (Building Information Modeling) in Architecture
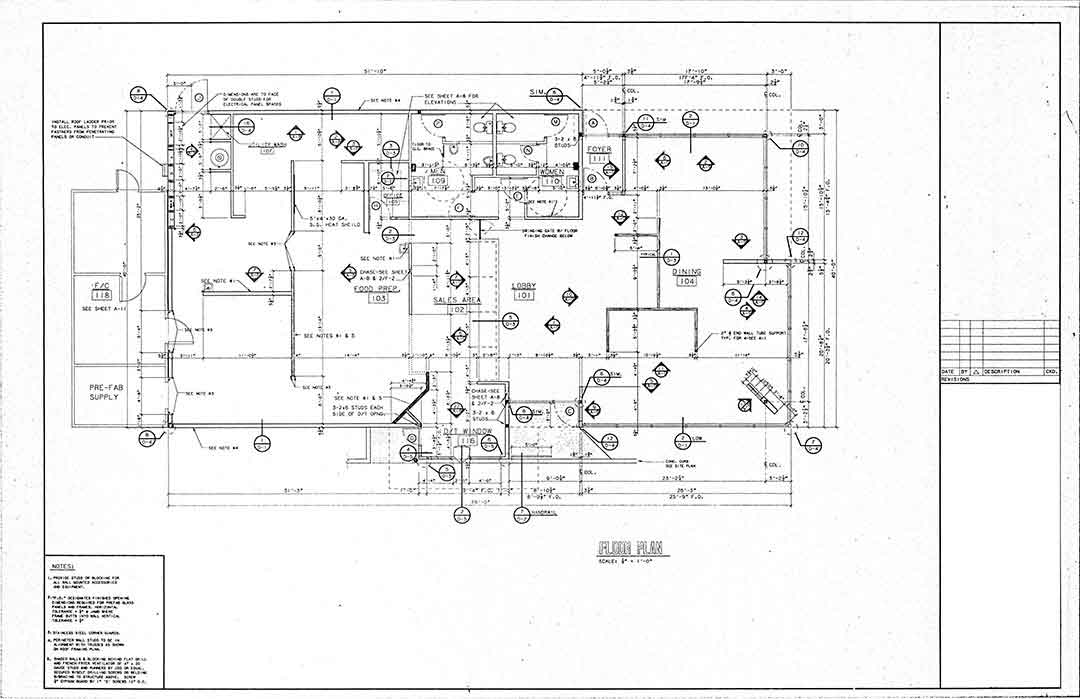
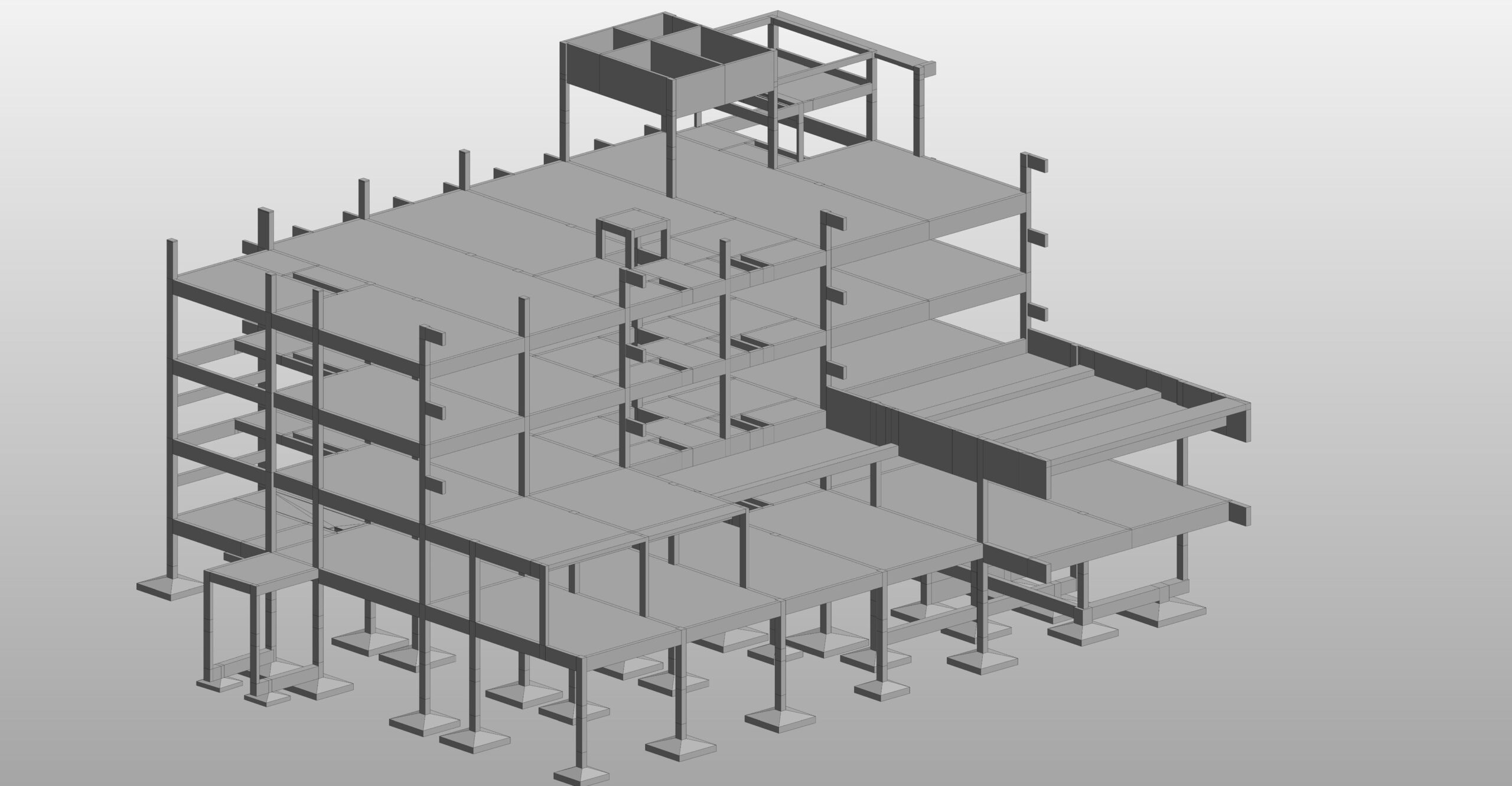
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a digital process used in architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) for designing, documenting, and managing building projects. It enables architects, engineers, and contractors to create and manage a 3D model that contains detailed information about a building’s components, materials, and performance.
Key Aspects of BIM in Architecture:
- 3D Modeling & Visualization:
- Architects use BIM to create detailed 3D models of buildings.
- It helps in visualizing the structure before construction begins.
- Data-Driven Design:
- BIM includes data like material specifications, costs, and energy efficiency.
- Architects can analyze and optimize building performance.
- Collaboration & Coordination:
- BIM allows multiple stakeholders (architects, engineers, contractors) to work on the same project.
- Reduces errors and improves communication.
- Clash Detection & Risk Reduction:
- Identifies potential clashes between structural, mechanical, and electrical components.
- Prevents costly rework during construction.
- Sustainability & Energy Efficiency:
- BIM helps in designing energy-efficient buildings.
- Simulations can predict energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Cost Estimation & Budgeting:
- Provides accurate cost estimates and material calculations.
- Helps in reducing waste and managing resources efficiently.
- Facility Management & Maintenance:
- After construction, BIM is used for facility management and maintenance.
- Helps in tracking building performance over time.
Popular BIM Software in Architecture:
- Autodesk Revit
- ArchiCAD
- Bentley AECOsim
- Vectorworks Architect
- SketchUp (with BIM extensions)