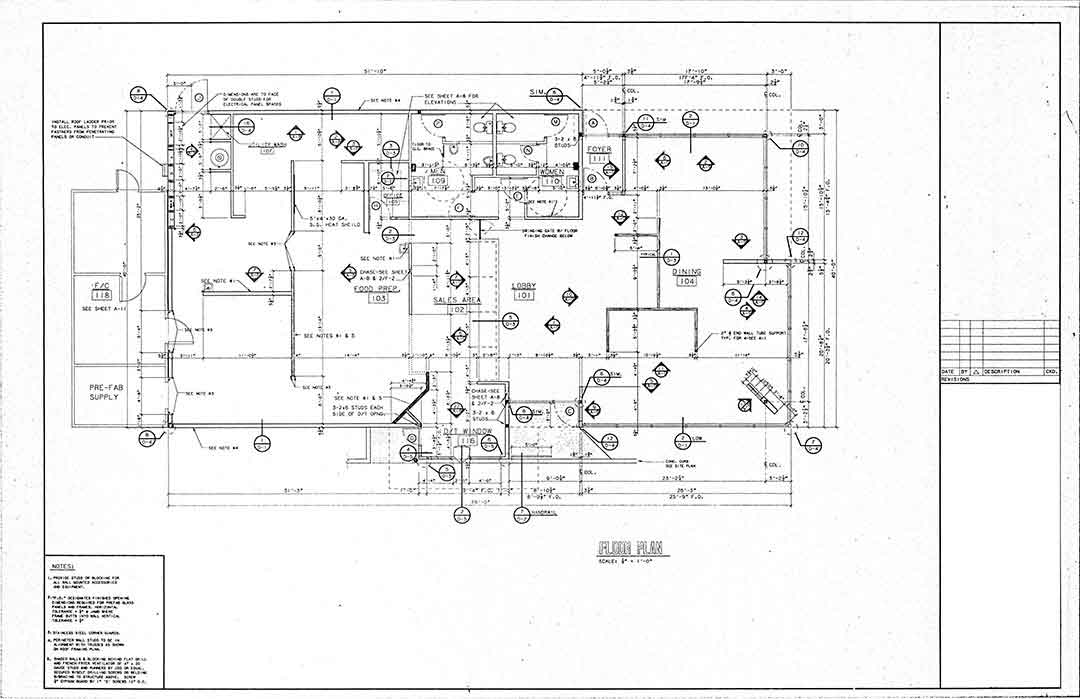
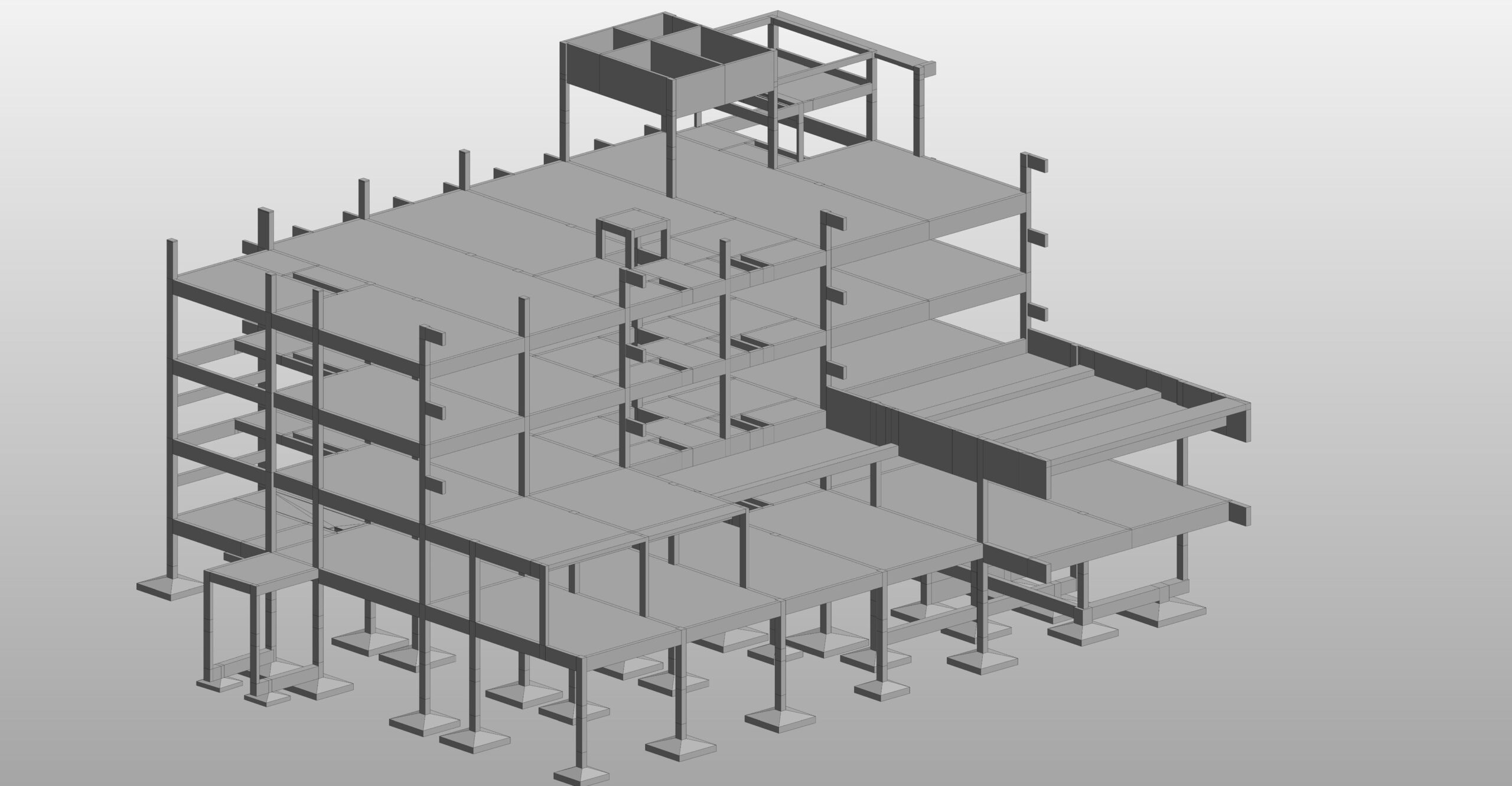
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is a technology used by architects, engineers, and designers to create precise 2D and 3D drawings of buildings and structures. It replaces traditional hand-drawn blueprints with digital models, improving accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility in the design process.
Types of CAD in Architecture:
- 2D CAD
- Used for creating floor plans, elevations, sections, and technical drawings.
- Examples: AutoCAD, DraftSight, BricsCAD
- 3D CAD
- Helps in visualizing and modeling buildings in three dimensions.
- Allows better understanding of space, materials, and lighting.
- Examples: AutoCAD 3D, SketchUp, Rhino 3D
- BIM-Integrated CAD
- Combines CAD with BIM for data-rich, intelligent modeling.
- Examples: Revit, ArchiCAD, Vectorworks
Benefits of CAD in Architecture:
✅ Precision & Accuracy – CAD software ensures exact measurements and reduces human errors.
✅ Faster Design Process – Saves time compared to hand-drawn blueprints.
✅ Easy Modifications – Changes can be made quickly without redrawing entire plans.
✅ 3D Visualization – Helps architects and clients visualize designs before construction.
✅ Collaboration & Integration – CAD files can be shared with engineers, contractors, and clients.
Popular CAD Software in Architecture:
- AutoCAD – Industry-standard for 2D and 3D drafting.
- SketchUp – Easy-to-use 3D modeling software.
- Revit – BIM-based CAD software for advanced architectural design.
- ArchiCAD – BIM-integrated CAD software.
- Rhino 3D – Great for complex and organic shapes in architecture.